Using EVM with MS Project 2016
Using EVM Capability of Microsoft Project 2016
Earned Value Management (EVM) is one of the well-defined project tracking methods. PMI® (Project Management Institute) recommends this technique in its book – PMBOK® Guide (Project Management Body of Knowledge Guide).
MS Project 2016 Professional and it earlier versions like MS Project 2013 and MS Project 2010 fully support EVM. Microsoft Project has inbuilt fields for all EVM measurements.
Earned Value Management
In Earned Value Management we track the cost and schedule performance by measuring three parameters – Planned Value (PV), Earned Value (EV) and Actual Cost (AC). EVM converts all progress into cost and compare these values to measure progress.
EVM Terms:
| EVM Terms | Explanation |
| Planned Value (PV) | Estimated value of the work planned to be spent as of today. |
| Earned Value (EV) | Value of the work that is completed as of today (PV of completed work) |
| Actual Cost (AC) | Total cost actually incurred as of today |
| Budget at Completion (BAC) | Total planned value of the project |
| Estimate at Completion (EAC) | Forecasted total project cost as of today |
| Estimate to Complete (ETC) | Estimated cost of the remaining work |
| Variance at Completion (VAC) | The variance of total project cost project as of today |
| EVM Terms | EVM Formula | Explanation |
| Schedule Variance | SV = EV – PV | Measure of schedule performance. –ve value indicate delay |
| Cost Variance | CV = EV – AC | Measure of cost performance. –ve value indicate cost overrun |
| Schedule Performance Index | SPI = EV/PV | Measure of progress achieved. Value less than 1 indicate delay |
| Cost Performance Index | CPI = EV/AC | Measure of value of the work completed. Value less than 1 indicate cost overrun |
| To Complete Performance Index | TCPI = (BAC-EV) / (BAC-AC) | Measure of cost performance to be achieved on remaining work to meet project objectives |
| Estimate to Complete | ETC = EAC – AC | Estimated cost of remaining work |
| Variance at Completion | VAC = BAC – EAC | Variance of total projected cost from budget |
| Estimate at Completion (EAC) | AC + Bottom up ETC | When original estimates are fundamentally flawed |
| Estimate at Completion (EAC) | BAC / Cumulative CPI | When observing no variance, will continue with same expenditure rate |
| Estimate at Completion (EAC) | AC + (BAC-EV) | When variance observed as of now will not be observed in future. Will complete the project in remaining budget of remaining work. |
Using EVM in MS Project
MS Project has all EVM term inbuilt and can be calculated at any point of time in the project life cycle. However to use Earned Value Management, we must remember few things…
Important things to remember for using EVM in MS Project 2016
-
Project schedule
We should prepare a project schedule and get the stakeholder’s concurrence on the same before executing it. For better progress monitoring, project scheduled be as detailed as possible. More the detailing we do, our progress measurement and forecast will be more precise and accurate.
-
Baseline
Once the project schedule is agreed up, we must baseline the schedule otherwise EVM parameters cannot be calculated. Establishing a performance baseline gives us a reference point to compare the project progress with respect to duration, efforts, cost and dates.
In case of multiple baselines, we should define the baseline against which we will measure the performance. Go to the File, choose Options, select Advance in left navigation panel and scroll down on the right panel until you see “Earned Value Options for this project”. Click on drop down for “Baseline for Earned Value calculations” and select the baseline you want to set for measuring progress.
-
Resource and resource rates
We must list all the resources in resource sheet, provide their cost or bill rates and assign them to tasks. As the EVM is a cost based measurement techniques, assigning resources to each task and defining cost or billing rate for each resource is necessary. We will not be able to measure performance of any task using EVM if either we have not assigned resources to the task or resource rates are not defined for the resources assigned to that task.
-
Updating accurate actual data
Obviously progress cannot be measured until actual progress data is updated. EVM tells us – are we delayed, on time or ahead of plan, are we over budget, on budget or under budget, at what rate we are progressing, how much more we need to spend to complete the project, forecasted cost at completion etc.? To measure these schedule and cost performance, it is important that actual data of accomplishment & cost is updated in MS Project in a timely manner. We should also update remaining duration or work for ongoing and future tasks if there is any change from the planned duration or work. Better the accuracy of actual data, better will be performance measurements.
EVM Measurements in Microsoft Project 2016
MS Project provide tables and reports to measure for EVM reporting. Following views, tables and reports can be used for EVM measurement and reporting
-
Earned Value Table
Earned Value table can be found as follows. Go to View Tab, click on Tables drop down and select More Tables to open More Table dialogue box. Select Earned Value. It will show following EVM measurements – PV, EV, AC, SV, CV, BAC, EAC and VAC for tasks scheduled in the project.
-
Earned Value Cost Indicator Table
Earned Value Cost Indicator table can be found as follows. Go to View Tab, click on Tables drop down and select More Tables to open More Table dialogue box. Select Earned Value Cost Indicator table. It will show following EVM measurements – PV, EV, CV, CPI, BAC, EAC, VAC and TCPI.
-
Earned Value Schedule Indicator Table
Earned Value Cost Indicator table can be found as follows. Go to View Tab, click on Tables drop down and select More Tables to open More Table dialogue box. Select Earned Value Schedule Indicator table. It will show following EVM measurements – PV, EV, SV and SPI.
-
Earned Value Report
Earned Value Report is a report that sketch earned value graph based on values of PV, EV and AC. It is a pictorial representation of progress from start of the project until date of measurement. It can be found as follows – Go to Report Tab, click on Cost drop down and select Earned Value Report. You can customize the report using Pivotal section of the report.
-
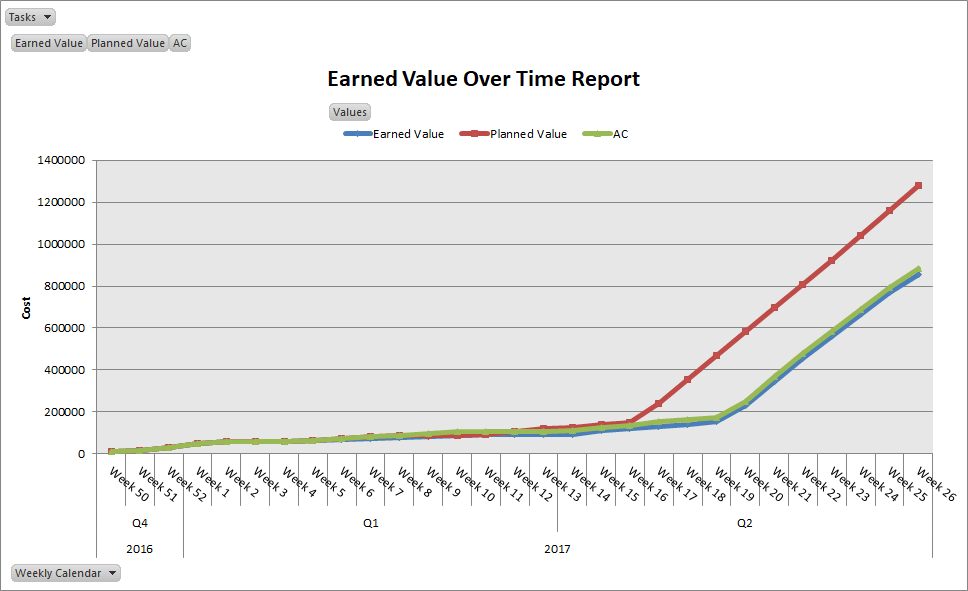
Earned Value Report Over Time
Earned Value Over Time Report is same as Earned Value Report and sketches earned value graph based on values of PV, EV and AC. It is a visual report and can be found as follows – Go to Report Tab and click on Visual Reports. It will open a Visual Report dialogue box. Select Earned Value Over Time Report. It will open an Earn Value graph in Excel. You can customize the report using Pivotal section and Assignment Usage Sheet.

Earned Value Graph in MS Project Reports
I hope it will make it convenient for you to use EVM with Microsoft Project. Please share your view and experience in the comments section below. I look forward to read your views.
Want to attend Microsoft Project 2016 Workshop – Click here
PMI, PMBOK and PMP are registered mark of Project Management Institute Inc.
4 thoughts on “Using EVM with MS Project 2016”
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
How do you determine timenow in plotting the EAC graph
Hi Christian,
Thanks for your question. I did not get your question exactly but if you are asking how to forecast time using EVM, my answer is that EVM is weak on schedule side and does not forecast time. Actually critical path method used to be used to forecast time and EVM was formulated to forecast cost.
There is an extension to EVM called Earned Schedule which is used to forecast time. the calculation is bit complex comparing to EVM but is a decent method to forecast time.
Dear Vivek,
The calculations of EVA will remain inaccurate as in MS Project, PV and AC (ACWP) fields are not capturing the cost resource.
Kindly advise on how to solve this. Also, the fixed cost field is not a substitute as it does not
Dear Nilay,
Thanks for your question. It is not like this. Cost resources are dealt bit differently. MS Project considers cost resources for calculating PV, EV and AC however, they might not got updated correctly. The planned value of a cost resources is specified when you assign a cost resource to a task. If you have just assigned the cost resource without specifying the planned cost, MS Project will take zero. Similarly just marking a task 50% complete or 100% completely does not reflect the actual cost. You need to go to Task Usages view and changes the table to cost table and enter actual cost you spent on cost resource.
There is no problem with MS Project in considering cost resource. It may be possible that user might not have complete understanding of cost resources therefore not providing planned and actual cost properly.